
Loan Guide

Loan Guide
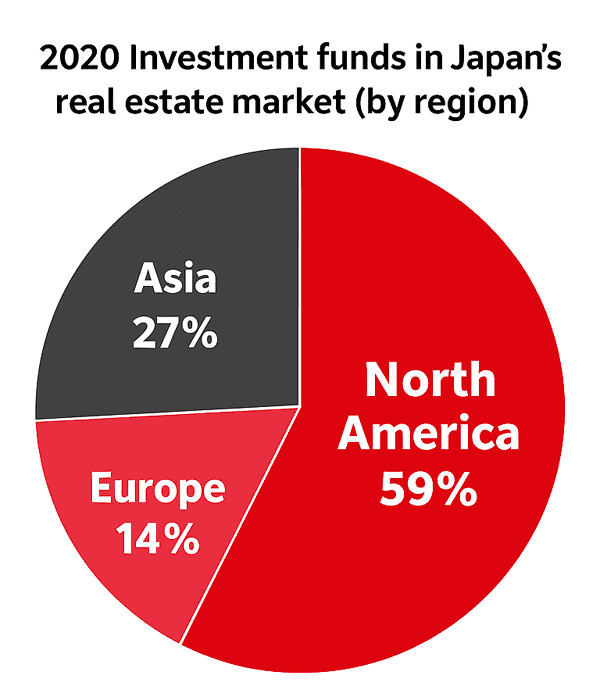
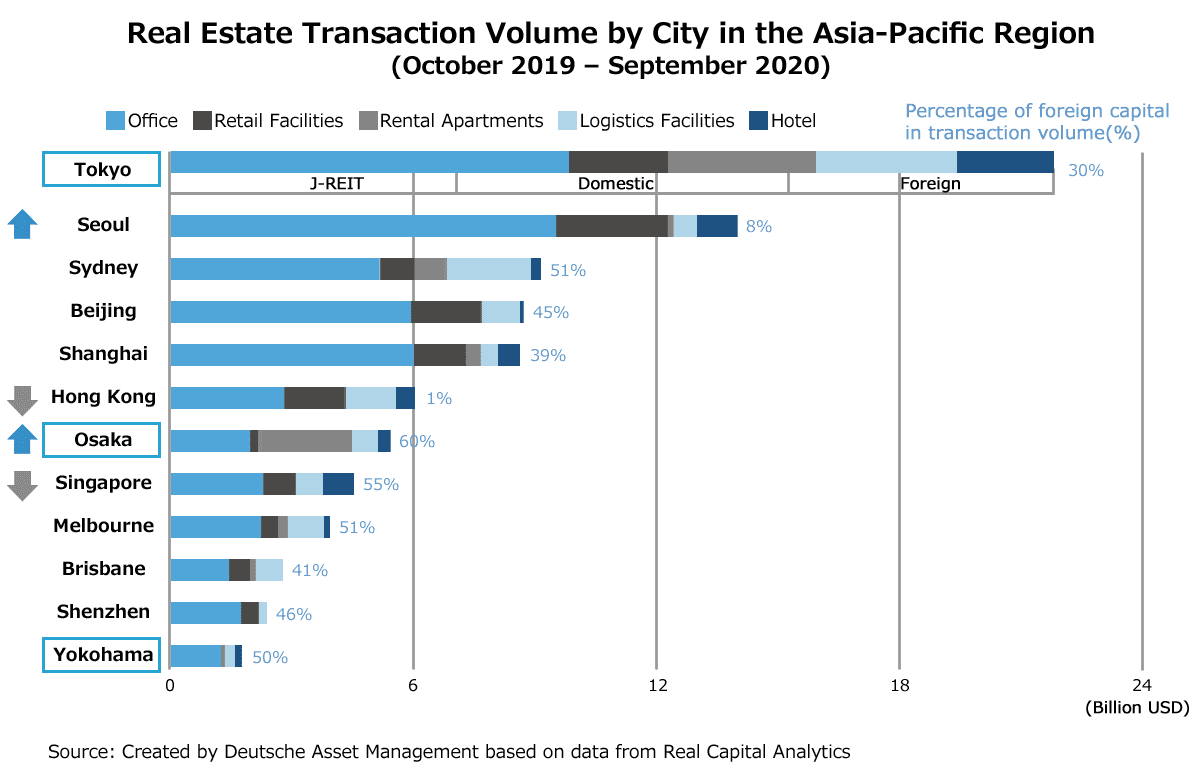
In many countries of the world, foreigners will face restrictions, like being banned altogether from owning land. However, Japan has no such restrictions tied to foreign ownership of real estate.
Taxes on property apply to foreigners and Japanese citizens the same way, and foreigners do not have to pay any special taxes just because they are foreigners. Foreigners can purchase property even if they do not have permanent residency or any kind of visa.
While Japan’s domestic mortgage market is well developed, foreign buyers face a unique set of challenges. For example, foreigners living outside of Japan (non-resident investors) often cannot obtain home loans in Japan. This is a very important fact that applies to non-resident foreign home buyers that isn’t too often fully understood.
For example, foreigners living outside of Japan (non-resident investors) often cannot obtain home loans in Japan. This is a very important fact that applies to non-resident foreign home buyers that isn’t too often fully understood.
For foreigners who live in Japan, you need to be aware that eligibility and conditions for loans will depend on many criteria including: permanent residency, type of visa, length of stay, and ability to speak Japanese.
When foreigners apply for home loans in Japan, banks assess several key factors related to the applicant’s financial situation and background. The most important of these is the applicant’s permanent residency status.
Here are the main factors Japanese banks consider when reviewing foreign applicants for home loans:
Home mortgages in Japan generally speaking will fall into two categories: fixed-rate and variable-rate, each with its pros and cons to consider before making your choice.
It’s important to understand the type of interest rate, repayment method, and whether it comes with a guarantee as you plan your mortgage.
Loan screening includes income, credit history, and debt-to-income ratio. For foreigners, additional factors include visa type, length of stay, and ability to communicate in Japanese. Foreigners in Japan without valid residence status will usually find it very difficult to obtain a loan from a Japanese lender, so it is important to check your eligibility before assuming you can borrow.
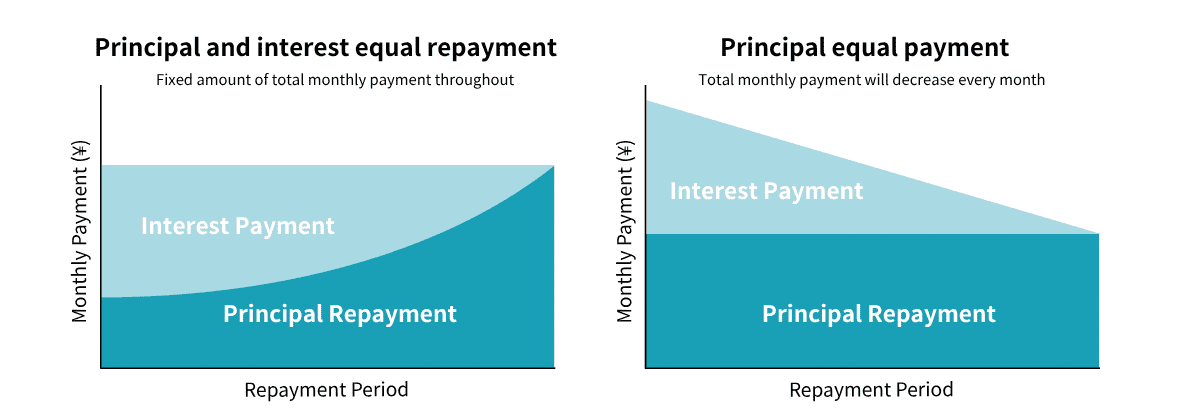
Many banks require borrowers to understand Japanese to sign contracts, so those with limited Japanese skills should consider using bilingual mortgage brokers.
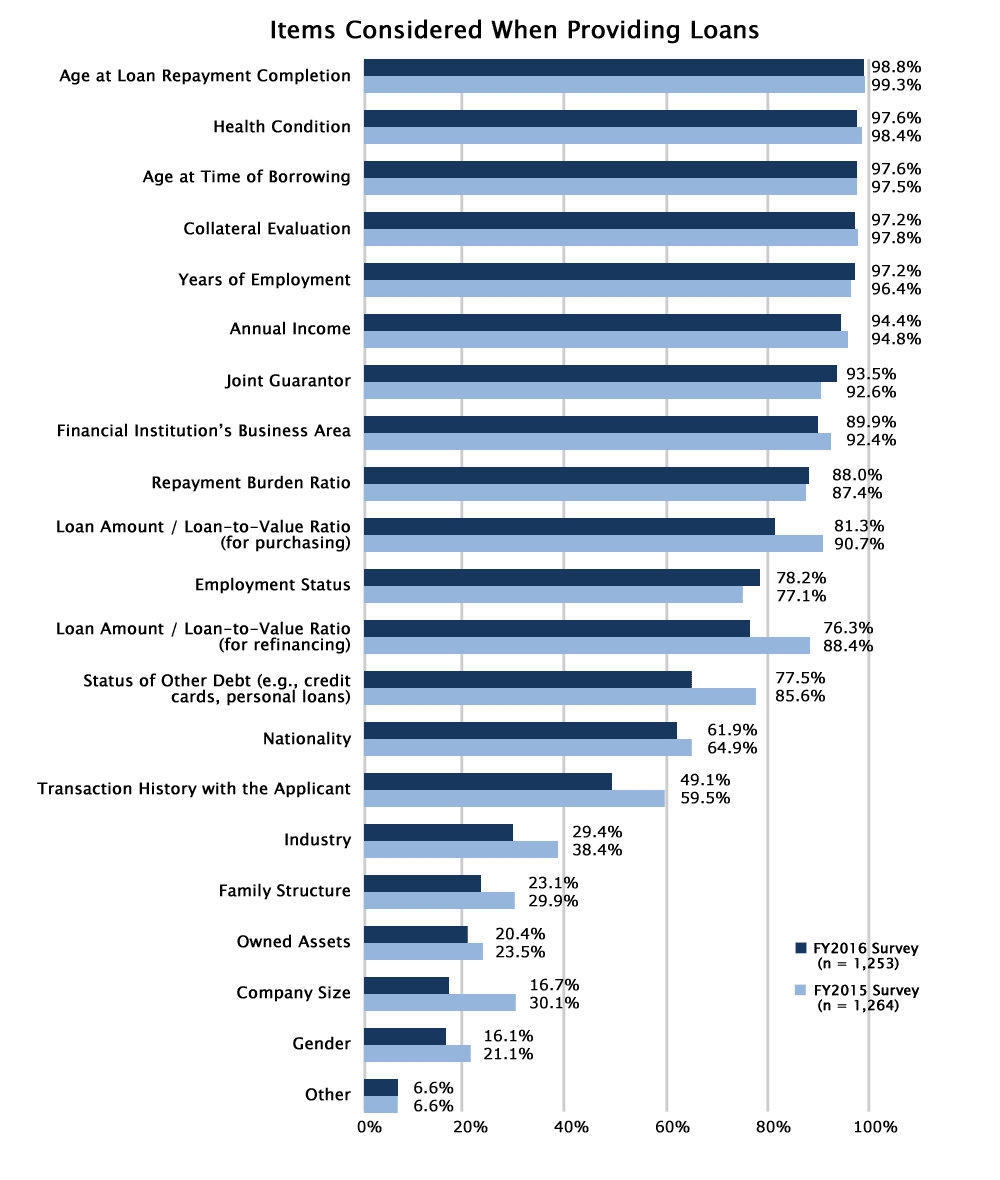
Major Japanese banks such as MUFG Bank, Mizuho Bank, and Resona Bank generally do not offer mortgages to non-permanent residents. However, some banks have introduced special loan products that allow non-permanent residents to apply if they meet certain conditions—such as being married to a Japanese national or having long-term residency.
| Requirement | Typical Expectation |
|---|---|
| Residency | Long-term visa or Permanent Resident (PR) status |
| Address | Registered address on a jūminhyō (住民票) |
| Employment | 2–3 years with current employer or 2–3 years of self-employment |
| Income | Usually ≥ ¥5 million (some banks accept ¥3–4 million) |
| Down payment | 20% standard; 30–50% often required without PR |
| Age | Loan must be repaid by age 75–80 |
| Documentation | Passport, zairyū kādo (residence card), gensen-chōshūhyō (tax certificate), bank statements, etc. |
| Insurance | Enrollment in dan-shin (group credit life insurance) |
Some banks offer specialized mortgage products designed for foreign residents without permanent residency. Notable examples include AEON Bank and Tokyo Star Bank, both of which provide options with more relaxed requirements compared to conventional loans.
For instance, AEON Bank outlines the following key eligibility conditions (partial list):
While loans may be available under these terms, they often come with stricter conditions such as a shorter repayment period (e.g., up to 15 years) and higher interest rates (e.g., base rate +1.0%, with no preferential rates). Similarly, Tokyo Star Bank offers mortgages to non-permanent residents with a maximum term of 35 years but typically with higher interest rates.
Other institutions such as Prestia (SMBC Trust Bank) also provide mortgage loans to foreigners without requiring permanent residency. Key conditions include:
Prestia does not require a guarantor and offers English-language support. Suruga Bank also welcomes consultations from non-permanent residents and actively supports foreign borrowers with English-language documentation. In general, these specialized financial institutions tend to offer higher interest rates and lower loan-to-value (LTV) ratios compared to major commercial banks.
If obtaining financing from a Japanese bank is not possible, foreign buyers may consider using banks in their home country or other international lenders. If your home country has banks that offer loans for purchasing Japanese property, that may be a viable option. In some cases, if your home country’s bank has a branch in Japan, you may be able to secure a mortgage through them.
The advantage of using a bank from your home country is that they can more easily assess your credit history and continue collections even if you move back abroad. However, note that the applicable interest rate will often be based on your home country’s standards, which may be higher than those in Japan, increasing your repayment burden.
In regions with high demand for Japanese property, such as Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore, some local banks (e.g., ORIX Asia Limited, Mega International Commercial Bank, UOB) offer mortgage products specifically for overseas buyers interested in Japan.
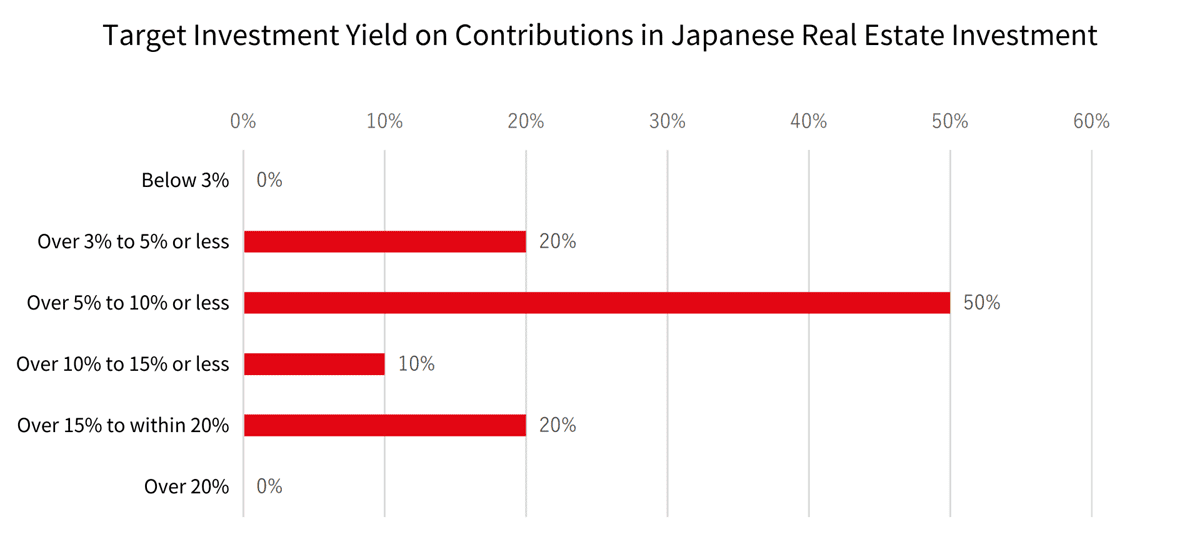
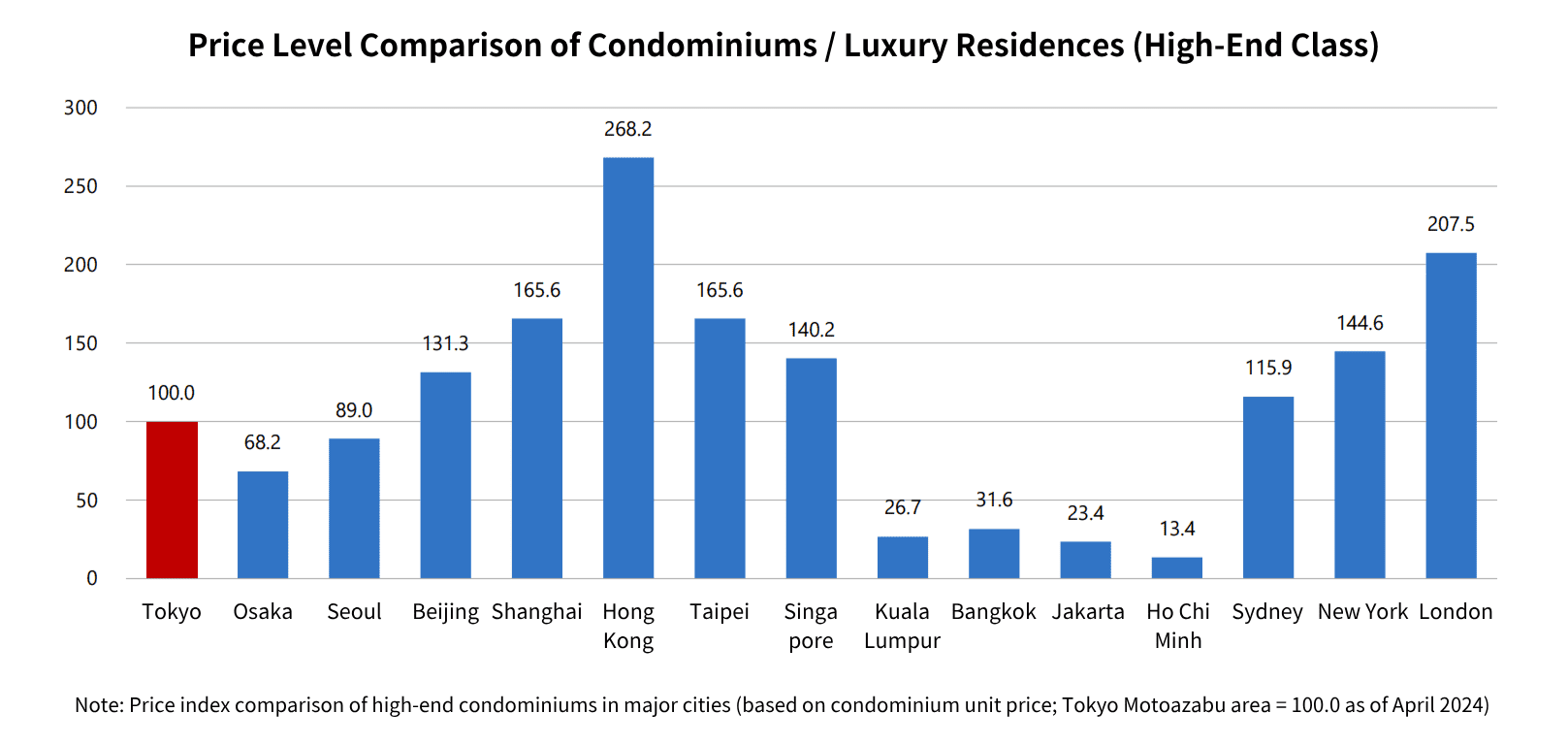
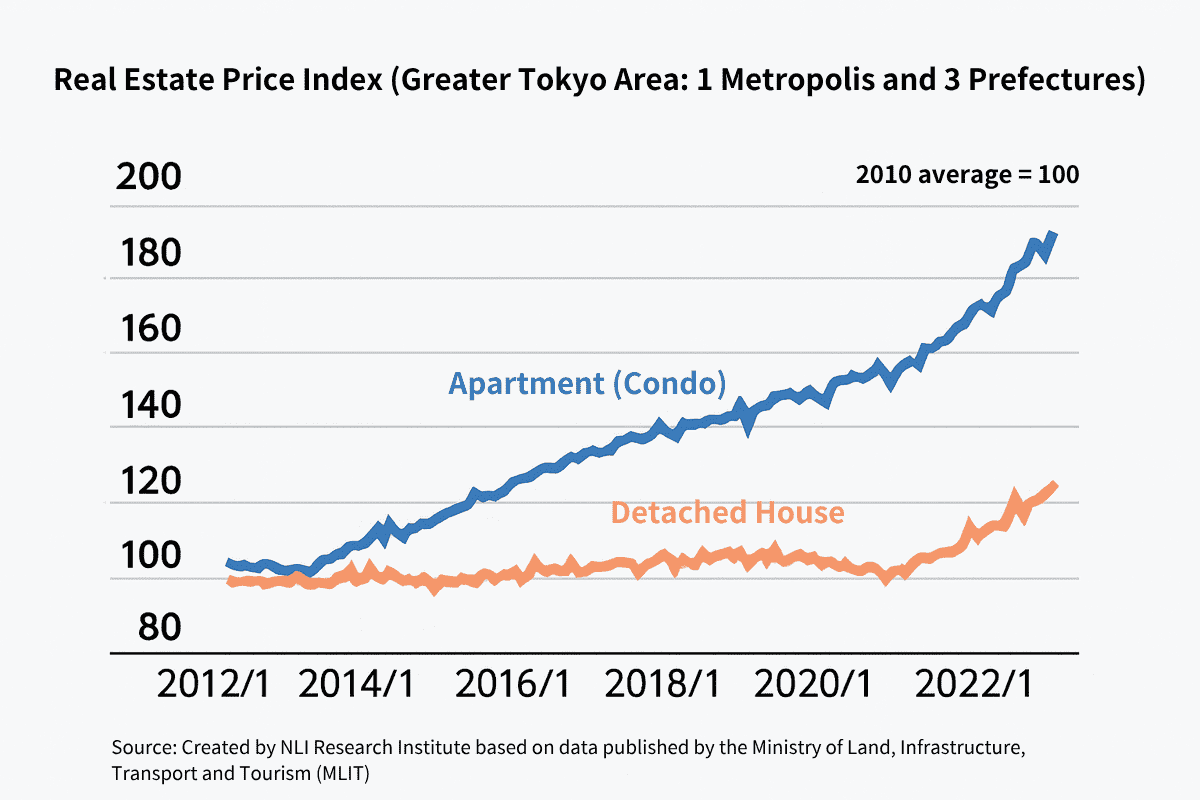
Compared to cities like Hong Kong, Singapore, and Taipei where real estate prices have surged, Japan offers relatively affordable properties with yields around 4–10%. From January to September 2020, real estate investment in the Tokyo metropolitan area totaled $19.4 billion, the highest worldwide.
Since home loans are not available for investment properties, real estate investment loans must be considered. Most Japanese lenders require permanent residency, but some provide loans without it if you meet conditions like having sufficient funds, residence period, employment years, and income. Screening conditions vary by lender; direct inquiries are recommended.
For non-resident foreign investors, one practical way to access real estate investment loans in Japan is by establishing a local Japanese corporation. By setting up a kabushiki kaisha (KK) or godo kaisha (GK) and purchasing property under the company’s name, the investor may be eligible for corporate real estate loans.
A real example is Shinsei Investment & Finance, a member of the SBI Shinsei Bank Group, which offers loans to Japanese corporations established by foreign investors. These loans are intended for companies funded and established by non-residents for the purpose of acquiring property in Japan.
Key requirements include:
Importantly, banks generally require the formation of a new Japanese corporation. Simply registering a Japan branch of a foreign company is usually insufficient, as branches are not considered separate legal entities under Japanese law and may not meet credit evaluation standards for lending.
Here are some major financial institutions offering real estate investment loans to foreign investors. Check the conditions for each institution to find the best option.
| Financial Institution | Loan Conditions | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Tokyo Star Bank, Ltd. | Loans for Japanese corporations established by foreign investors and foreign nationals with resident status investing in Japan. | Official Website |
| Shinsei Investment & Finance Ltd. | Personal loans for non-residents holding Hong Kong or Japanese passports residing in Hong Kong. | Official Website |
| ORIX Bank Corporation | No permanent residency required; for foreigners residing in Japan with an annual income over 7 million yen. Property conditions apply. | Official Website |
| Prestia (SMBC Trust Bank) | No permanent residency required; foreigners residing in Japan with annual income over 7 million yen. No guarantor needed. Property conditions apply. | Official Website |
| United Overseas Bank Limited | For foreign investors. | Official Website |
| Bank of China Ltd. | For Chinese nationals residing in Japan. | Official Website |
| Bank of Communications Co., Ltd. | For foreigners residing in Japan with income over 4 million yen. | Official Website |
A: Generally, no. Most Japanese lenders require applicants to hold a valid visa and reside in Japan. Therefore, overseas investors typically are not eligible for home loans in Japan.
A: Very difficult. Lenders require proof of stable long-term residence, employment, and income. Short-term visa holders often face rejection or strict terms.
A: Some banks offer limited English support, but Japanese is generally required. Using bilingual brokers or professional translators is strongly recommended.
Japan’s mortgage market is gradually improving access for foreign buyers but strict residency requirements remain. Overseas investors rarely get direct financing from Japanese banks and must plan accordingly with alternative funding strategies. Keeping updated on lender policies and seeking expert advice are keys to successful property financing in Japan.
Note: All conditions and figures are based on information as of 2023–2024 and are subject to change. Please consult with individual financial institutions for the most up-to-date information.
Once you understand how mortgages and home loans in Japan work, the next step is to learn the full process of buying a house in Japan. Our Property Buying Guide explains each step clearly, from selecting properties to preparing documents and completing contracts. Designed for foreign buyers, this guide helps you navigate the Japanese real estate purchase process with confidence.